/>
How long will the outbreak last?
We cannot predict the length of the outbreak nor how it will evolve. This is a new pathogen, of which we still have limited knowledge. For example, we do not know whether its spread in the community will be limited during the summer, as is the case with seasonal flu.
Transmission
Where do coronaviruses come from?
Coronaviruses infect animals; however, some of them also infect humans. Rarely, strains identified in animals can be transmitted to humans, with the exception of MERS, SARS, and currently, Covid-19.
How is the virus transmitted and how easily can the disease spread?
Although the virus comes from animals, it can be transmitted between humans, and it can easily spread in the community. A spread in the community means the identification of confirmed cases for which the source of transmission is unknown. Strictly practising social distancing while implementing other measures of self-protection may limit the rate of spread in the community.
Can a confirmed case of novel coronavirus transmit the disease (Covid-19) to other persons?
The virus is transmitted from human to human, therefore, a person with signs and symptoms compatible with Covid-19 infection may transmit the disease to other people. This is why isolation at the hospital or at home is advised for patients with symptoms, depending on the severity of their clinical condition. Patients are not considered infective and can, therefore, be removed from isolation when ALL CRITERIA BELOW are met: They are afebrile without taking any antipyretics. They show no symptoms (AND no cough)
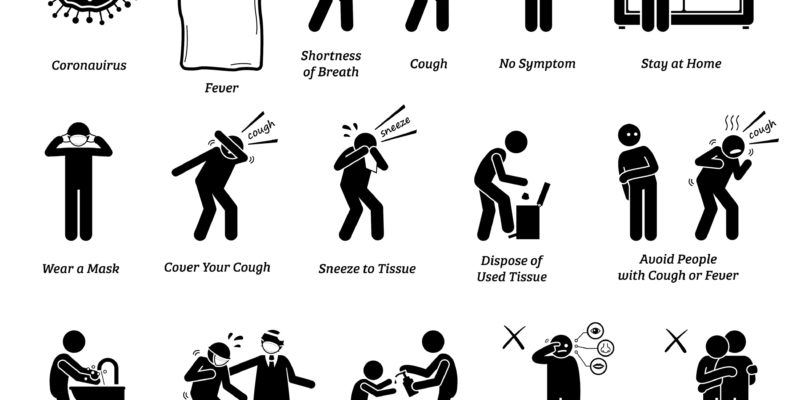
Can a person in quarantine transmit the disease to others?
Quarantine is an isolation measure used for individuals or a group of people possibly exposed to a pathogen but not showing any symptoms; the aim of isolation is to prevent transmission. Quarantine duration is the same as the disease incubation period, which is the time between last exposure to the pathogen and display of symptoms. Covid-19 incubation period is 14 days. Persons who are taken off quarantine can no longer transmit the disease.
Can Covid-19 be transmitted through food?
(refrigerated or frozen food included)
Covid-19 is transmitted from human to human through respiratory droplets (e.g. cough, sneeze, runny nose). There are no indications of transmission through food.
However, it is necessary to wash your hands with soap and water
-before cooking or consuming food
-after coughing, sneezing or blowing your nose
-after using the toilet.
It may be possible that a person can be infected with the disease by touching surfaces contaminated by the novel Covid-19 coronavirus and then touching their own mouth, nose or eyes; however, this is not the primary way of transmission. Nevertheless, due to the virus poor survival on surfaces, transmission through food or packages that have been handled in the past days or weeks in ambient temperature or under freezing or deep-freezing conditions is considered unlikely.
Can improved weather conditions (higher temperature) limit the spread of novel coronavirus Covid-19?
We do not yet know if weather improvement and higher temperatures may limit the spread of novel coronavirus Covid-19. Other viruses, such as those of seasonal influenza or common cold are easier to spread during the cold months; however, this doesn’t rule out the possibility of infection during warmer periods.
What does “community spread” mean?
A spread in the community means the identification of confirmed cases for which the source or way of transmission is unknown.
What shall I do if I come in close contact with a confirmed case of novel coronavirus COVID-19?
If you have come in close contact with a confirmed case of new coronavirus COVID-19, you should stay at home for a period of 14 days from last contact and monitor your health. I
If you show symptoms compatible with Covid-19 infections such as fever, cough, difficulty breathing you must contact your doctor immediately
Which groups are at high risk of severe infection with Covid-19 coronavirus?
High-risk groups consist of elder people as well as people of any age with an underlying chronic condition such as cardiovascular and lung diseases, diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency.
What should people in high-risk groups do?
People in high-risk groups must systematically implement all measures for preventing the transmission and spread of the new coronavirus Covid-19. If you belong to a high-risk group, you should do the following:
– Avoid contact with persons who show signs and symptoms of a respiratory infection.
– Avoid all unnecessary travels, particularly to areas or countries with confirmed virus spread in the community.
– Implement hand hygiene and avoid touching your own face with your hands (eyes, nose, mouth)
– Adhere to chronic medication regimen (if available) and to your doctors’ advice.
– Avoid gatherings and events, unless necessary.
– Contact your doctor immediately in case you develop symptoms of respiratory infection; seek medical evaluation.
– Avoid visits to patients in hospitals.
– Avoid visits to healthcare units without severe reason.
Can masks effectively protect against the new COVID-19 virus?
Using a mask can prevent the disease from spreading from patients to healthy individuals. Therefore, masks are used only for the protection of
– healthcare professionals
– caregivers, attending to patients with Covid-19 infection (e.g. at home, in chronic care facilities)
Healthy individuals are not advised to use masks.

Is it safe to receive packages or parcels from China or other areas where the virus has spread in the community?
Given that SARS-Cov2 cannot survive on surfaces for a long period of time, the risk of transmission from products or packages that have travelled for days or weeks in ambient temperature is low. Coronaviruses are mainly transmitted through respiratory droplets.
There are currently no indications suggesting SARS– CoV2 transmission through contact with products/ packages imported from affected areas, nor are there any reported cases associated with such a way of transmission.
How can I protect myself against COVID-19?
Wash your hands regularly and thoroughly with soap and water or a disinfectant and avoid touching your face (eyes, nose, mouth) with your hands.
Cover your cough or sneezes with a tissue which you must dispose of straightaway using a rubbish bin. If you don’t have a tissue, use your elbow.
If you experience mild symptoms of respiratory infection (cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat) stay home in isolation.
If symptoms become worse or if you are considered high-risk (elderly or people of any age with underlying health conditions e.g. diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular and chronic respiratory diseases, arterial hypertension), you should immediately contact your physician for evaluation.
If you are under medication, you must comply with your doctors’ advice.
You should not come in contact with people who show symptoms of respiratory infection (cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat).
Avoid gatherings, social events, visits to other houses and crowded open spaces.
Avoid any unnecessary travels abroad or within the country.
Do not visit your doctor or a health unit if you develop mild symptoms of a respiratory infection (cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat).
Strictly avoid visits to patients in hospitals.
Strictly avoid contact with people in high-risk groups. If this is not possible, take all personal hygiene measures (wash your hands thoroughly, use a mask or keep a 2-meter distance from one another).
Symptoms – Laboratory investigation
What are the symptoms of the new coronavirus Covid-19 infection?
Based on the available data, the virus can cause mild flu symptoms such as:– fever
– cough
– difficulty breathing
– muscle pain
– fatigue
In severe cases, patients may develop pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis and septic sock and death. People in high-risk groups (e.g. elders, patients with heart conditions, diabetes mellitus, liver or lung conditions) are more likely to develop severe symptoms of the disease.
When should I get tested for new coronavirus Covid-19 infection?
If you show symptoms such as fever, cough and difficulty breathing, you should stay at home and contact your doctor immediately.
Laboratory investigation for the new coronavirus Covid-19 is advised for:
– patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Illness who are in need of hospitalization or are currently hospitalized
– patients in hospitals or elderly care or chronic care units who develop an acute respiratory infection with fever, cough or dyspnea
– healthcare personnel who develop an acute respiratory infection with fever
– elderly people (> 70 years old) or individuals with severe chronic underlying conditions (e.g. chronic pulmonary disease, chronic heart disease, – – diabetes mellitus, severe immunodeficiency) who develop an acute respiratory infection with fever and cough or dyspnea.
Can lab tests for infection with new coronavirus Covid-19 come out negative at first and positive later?
When lab tests for the new coronavirus Covid-19 come out negative, this means that the virus has not been detected in the sample. This can happen at the early stages of the disease. During the symptomatic phase and while the disease progresses, lab tests may come out positive. If a patient with symptoms compatible with Covid-19 infection is submitted to laboratory investigation that comes out negative, then the disease is attributable to other causes and not Covid-19.

Treatment – Vaccination
Is there a treatment for COVID-19 infection?
There is no designated treatment for the disease. Treatment is symptomatic, aiming to relieve symptoms (e.g. fever, difficulty breathing). International literature on the use of antiviral drugs against the new coronavirus is very limited and comes almost exclusively from China. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate a possible therapeutic action of certain pharmaceutical substances against coronaviruses resembling the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. However, there are currently no sufficient data from randomized clinical studies in humans with the use of control groups, supporting the administration of any drug in patients with suspected or confirmed infection with the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. According to the 6th edition of Guidelines by China’s National Health Commission on the empirical treatment of COVID-19, the following antiviral drugs are suggested: inhaled interferon-alpha (IFN-α), lopinavir/ritonavir, chloroquine phosphate, ribavirin and arbidol (broad-spectrum antiviral drug).
Is there a vaccine for COVID-19?
At the moment, there is no available vaccine for COVID-19. This is why timely diagnosis and implementation of measures against the spread of the disease are of vital importance. Several pharmaceutical companies are working towards developing a vaccine; however, it will take a long time until their work is finalized.
Can the vaccine for seasonal influenza protect against COVID-19?
The influenza vaccine does not protect against COVID-19. However, given that we are currently going through the seasonal flu peak, the influenza vaccine is the best way to protect ourselves against the seasonal flu.
Source: National Public Health Organization. You may read the above in Greek language here
